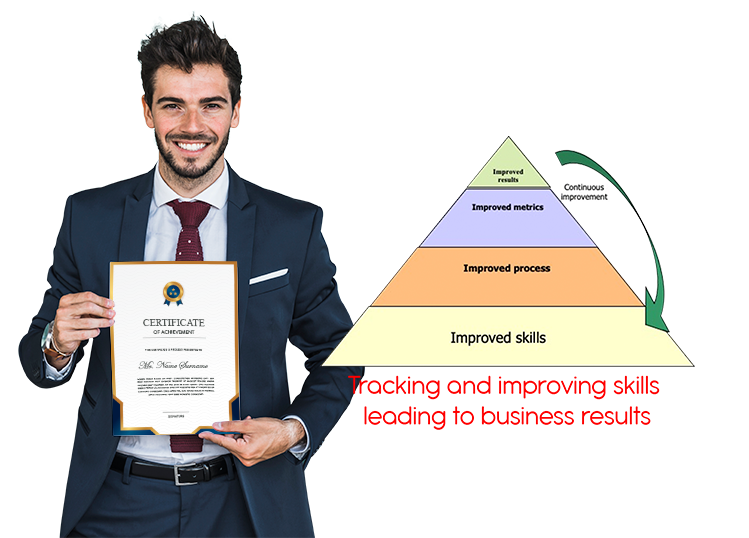
Based on these factors
elicitation, modeling and documentation, change management
goals, timelines, tasks, resources, progress, risks, quality, coordination, stakeholders, deadlines.
expert judgment, analogy, parametric, agile, bottom-up, top-down.
creating project schedules and tracking projects using schedules
identification, assessment, prioritization, mitigation, monitoring, control, analysis, planning, response, communication.
planning, execution, defect tracking, quality assurance, verification, validations.
Based on these factors

elicitation, modeling and documentation, change management

goals, timelines, tasks, resources, progress, risks, quality, coordination, stakeholders, deadlines.

expert judgment, analogy, parametric, agile, bottom-up, top-down.

Creating project schedules and tracking projects using schedules
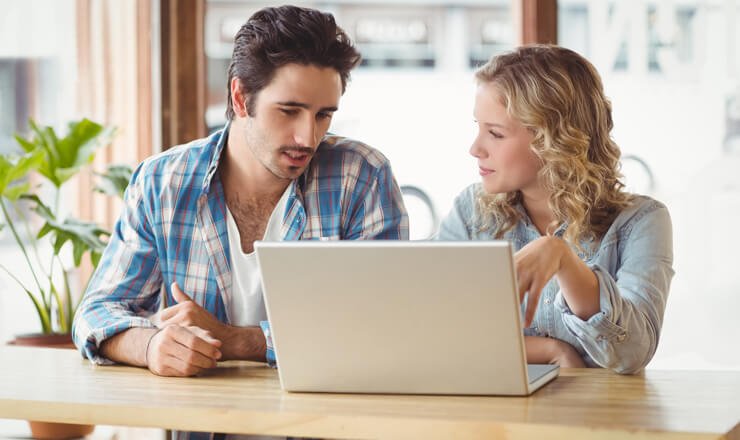

identification, assessment, prioritization, mitigation, monitoring, control, analysis, planning, response, communication.
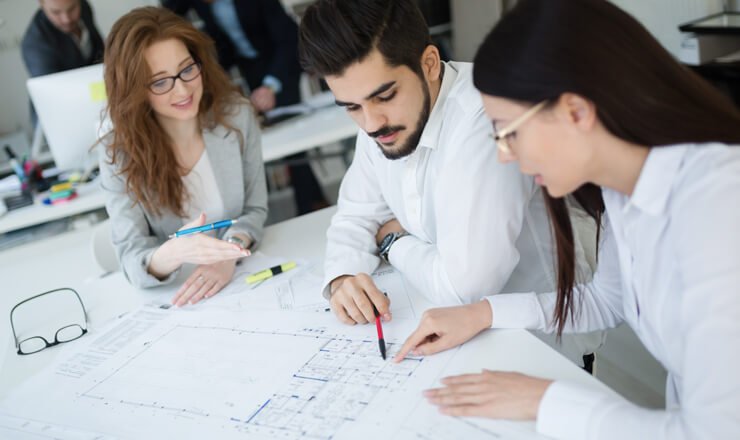

planning, execution, defect tracking, quality assurance, verification, validations.
The prevalent project management certificates don’t directly measure the ability of a software project manager to deliver software projects. Hence, there is a need for an exam that directly tests the capability to deliver software projects efficiently. The most prevalent project management certificates today are PMP and PRINCE2 apart from several agile certifications such as CSM, CSPO, PMI-ACP, SAFe, DSDM have limitations. PMP and PRINCE2 frameworks are generic project management bodies of knowledge and tests a person for knowledge in general concepts of project management. However, for a person certified as PMP to be effective in software delivery he has to acquire much more software specific knowhow in project management.




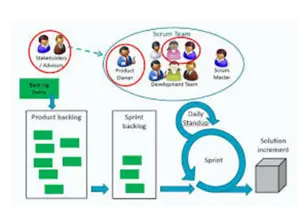
For instance, software sizing and estimation techniques software life cycle models, software requirements engineering, software engineering methodologies such as OOSE and so on are unique to the software field. A PMP has to be knowledgeable to a good extent in these fields to be effective as a software project manager. Hence, a certification beyond PMP is needed. On the other hand, agile certifications measure the knowledge in agile methodologies and don’t cover the complete gamut of project management. A project manager must be knowledgeable about requirements engineering, estimation techniques other than story points also, risk management, software engineering, stakeholder management, software testing and so on. Even though a software project manager need not necessarily be proficient in all the above aspects, he should have some sound knowledge. Please refer to this article on skills of software project managers for more details on why and to what extent a software project manager should possess these skills.
Hence, neither the PMP andPRINCE2 certifications nor Agile certifications cover the complete software project management gamut and the ACE PMP certification fills this void.







ACE best practices at level 1

ACE best practices at level 2

ACE best practices at level 3

ACE best practices at level 4
OUR SERVICES
Use summarization quizzes
Maintain and demonstrate
Follow preacher’s principle







